
6
Tutorial--The Insight Environment

This section describes lessons on using the DMol commands in the Insight environment. (Lessons on using the Insight interface are contained in the Insight documentation.)

Pilot online tutorials
Tutorials are available on-screen for use with the Pilot interface. To access the online tutorials for the DMol program, click the mortarboard icon in the Insight interface.
Then, from the Open Tutorial window, select DMol tutorials (in release 95.x) or Quantum Mechanics Tutorials and then DMol Tutorials (in release 4.0.0) and choose from the list of available lessons.
You can access the Open Tutorial window at any time by clicking the Open File button in the lower left corner of the Pilot window.
For a more complete description of Pilot and its use, click the on-screen help button in the Pilot interface or refer to the Insight II User Guide.

Overview of tutorial lessons
In Lesson 1: Unconstrained Optimization of Acetone in Cartesian Coordinates, you will be introduced to the process of setting up and running a DMol job via the Insight interface and will perform an unconstrained geometry optimization on acetone.
The topics covered in this lesson include:
Lesson 2: Constrained Optimization of Acetone in Cartesian Coordinates is similar to the first lesson, except that you will set a distance constraint before optimizing the geometry.
The topics covered in this lesson include:
In Lesson 3: HSOH Geometry Optimization, you calculate the optimized geometry of a tetratomic molecule with C1 symmetry, hydrogen thioperoxide. HSOH is the simplest molecule that contains a classical S-O single bond. Most small molecules that contain an S-O bond (e.g., SO, SO2, and HSO) also exhibit more energetically stable multiple S-O bonding. Thus, the characteristics of the S-O single bond are of theoretical interest. Additionally, hydrogen thioperoxide may be an important intermediate species in the atmospheric chemistry of acid rain.
The topics covered in this lesson include:
The lesson on transition-state optimization for H2 dissociating on a copper dimer using C2v symmetry, demonstrates a transition-state optimization calculation for the reaction:
Cu2 + H2 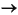 Cu2H2
Cu2H2
This test case was taken from a publication by Harris and Sandersson (1985), who mapped out the potential energy surface for the reaction without doing an optimization at the transition state.
The tutorial also shows how to use C2v point group symmetry to speed up energy calculations and to limit the conformational space in the geometry optimization. The total number of degrees of freedom will be 3 (2 for the hydrogen atoms and 1 for the copper atom).
Another tutorial illustrates the density of states functionality, which is a tool for analyzing the total and partial DOS, for a metallic system.
In the final tutorial, Thermochemistry and Properties of H2O, you optimize the structure and calculate thermochemical and molecular properties of a water model.
The topics covered in this lesson include:

Last updated September 25, 1997 at 03:13PM PDT.
Copyright © 1997, Molecular Simulations, Inc. All rights
reserved.





 Cu2H2
Cu2H2