

| DMol |


Several general requirements for running a background job on a remote host are:
The network queuing system and background jobs
Background jobs are often started from the Insight interface in immediate submission mode; that is, the job is run on the selected machine immediately upon submission. However, background jobs can also be submitted to a queue. The queueing mechanism pulls jobs from the queue and starts them on one of the machines available for the queue. Typically, each job is run to completion before the next job is pulled off the queue. Support for the network queuing system (NQS) is now available to allow you to submit background jobs to a queue on a local or remote machine.
The DMol image (and that of most other MSI quantum products) is encapsulated in a csh shell script which allows customization. Some of the features added to DMol 96.0/4.0.0 by the script are:
Shell scripts and utilities

The basis set input datafile packaged with DMol, named atom92.inp, contains input for extended basis sets for all atoms up to U. Its contents are summarized under Basis set summary. This input file is stored in $BIOSYM/data/dmol.
For example, suppose the molecule CH3F is to be calculated in DMol using the VWN local correlation and the B88 gradient-corrected exchange energy. An inatom file is created containing this Hamiltonian information and input for the atoms H, C, and F. The resulting basis set file in the local directory is called basis. Output from the DAtom calculation appears in the file outatom.
Overview
Double-numerical (DN) basis sets, that is, sets with twice as many atomic orbitals as are occupied in the free atom, are generated by solving the atomic DFT equations once for the neutral atom and again for the atom with a +2 charge. The ionic wavefunctions are then orthogonalized to those of the neutral atom. This method provides a way of generating basis sets that increase the electron density in the region close to the atom where bonding effects are important. The orthogonalization can result in the removal of functions that would otherwise form a linearly dependent set. Hence, these DN basis sets are not always exactly twice the size of minimal bases. However, because these functions are essentially exact for the atom, they are significantly more accurate than the analogous Gaussian or Slater atomic bases.
Input
When DAtom is used as explained above, input is in the inatom file and output is in the outatom file. The results (numerical basis functions) are stored in the basis set file.
> dmol run_name basisDefault basis set file
When run through the Insight interface, DMol no longer creates a basis set file; instead, the DMol background job makes a basis set file as needed, during the run (as does DMol in standalone mode).
> dmol run_nameHow DAtom runs within DMol
The DAtom utility is now integrated into DMol. First, it copies the appropriate input from atom92.inp to a local file called run_name.inatom. Next, DAtom generates a basis set as a run_name.basis file, and the output is stored in run_name.outatom. After a successful DMol run, these three files are removed from the working directory.
It is possible to carry out calculations with heavy atoms up to uranium (Z = 92). However, basis sets for heavy atoms are less accurate, since relativistic effects are not incorporated into the current version of DMol. In addition, the design of the basis set, definition of frozen orbitals, and choice of the polarization functions is not yet well established for these atoms. To facilitate design of basis sets, an additional file, named fzminpol.dat and located in $BIOSYM/data/dmol, has been introduced.
The $BIOSYM/data/dmol/fzminpol.dat file contains information about the frozen orbitals, minimal basis set, and polarization functions for all atoms up to uranium. You can overwrite the default values of the fzminpol.dat file by editing a copy of this file in your working or home directory.
Iatom f-inner f-all minimal polarwhere Iatom is the atomic number, and f-inner, f-all, minimal, and polar define the highest atomic shells for the frozen inner-core, frozen all-core, minimal basis, and polarization set, respectively. The atomic shells can be identified as usual by three numbers n, l, m. For example, the entry for the titanium atom is:
22 210 310 400 410Here, 22 is the atomic number for titanium. The 210 indicates that the 1s, 2s, and 2p atomic shells are frozen for the inner-core approximation, and the 310, that the 3s and 3p are additionally frozen for the all-core model. The minimal basis set for Ti atom includes the 4s (400) orbital, and the polarization function of the atom is 4p (410).
The complete fzminpol.dat file can be seen by examining the $BIOSYM/data/dmol/fzminpol.dat file with the UNIX more command or with any text editor.
The inatom input file
All input to DAtom is read from a file named inatom.
| 1
For hydrogenic orbitals (istart = -1), nprinc and lorb are hydrogenic functions to be included unchanged.
|
Example--Extended basis sets for selected atoms
The following sample input and comments illustrate the use of DAtom in generating basis sets.
INPUT -Comments
jmw Use Janak-Morruzi-Williams Hamiltonian.
1., 0, 0, 0, 0, Normal run for hydrogen.
1., 0, 0, 1, 2, Start with previous orbitals; compute spin energy.
1.3, 2, 0, -1, -1, Generate hydrogenic orbitals with z = 1.3 for use as
extended basis set; orthogonalize to existing orbitals.
1, 0, 0., 0., Use a 1s hydrogenic orbital.
2, 1, 0., 0., Use a 2p hydrogenic orbital.
3., 0, 0, 0, 0, Normal run for Li.
3., 0, 0, 1, 2, Start with previous orbitals, compute spin energy.
3., 2, 0, 1, -1, Start with previous orbitals; compute orbitals using
new occupation to be specified on next 2 lines;
orthogonalize before writing out.
2, 0, -1., 0., Remove one alpha electron from 2s.
2, 1, 0., 0. Use a 2p with unchanged occupation.
5., 3, 0, -1, -1, Generate hydrogenic orbitals using Z = 5, for
use as polarization and extended functions.
3, 2, 0., 0. Use 3d.
2, 1, 0., 0., Use 2p.
1, 0, 0., 0., Use 1s.
7., 3, 0, -1, -1, Generate hydrogenic orbitals using Z = 7, for use
as polarization and extended functions.
3, 2, 0., 0. Use 3d.
2, 1, 0., 0., Use 2p.
1, 0, 0., 0., Use 1s.
6., 0, 0, 0, 0, Normal run for carbon.
6. 0, 0, 1, 2, Start with previous orbitals, compute spin energy.
6., 1, 0, 1, -1 Start with previous orbitals; generate orbitals using
new occupation specified by 1 line (this will be C+2).
2, 1, -2., 0. Remove 2 alpha electrons from 2p.
5., 3, 0, -1, -1, Generate hydrogenic orbitals using Z = 5, for
use as polarization and extended functions.
3, 2, 0., 0. Use 3d.
2, 1, 0., 0., Use 2p.
1, 0, 0., 0., Use 1s.
7., 3, 0, -1, -1, Generate hydrogenic orbitals using Z = 7, for
use as polarization and extended functions.
3, 2, 0., 0. Use 3d.
2, 1, 0., 0., Use 2p.
1, 0, 0., 0., Use 1s.
11., 0, 0, 0, 0, Normal run for sodium.
11., 0, 0, 1, 2, Start with previous orbitals, compute spin energy.
11., 4, 0, 1, -1 Start with previous orbitals; generate orbitals using
new occupation specified by next 4 lines; this will be
Na+2 with extended functions.
2, 1, -1., 0. Remove one alpha electron from 2p.
3, 0, -1., 0., Remove one alpha electron from 3s.
3, 1, 0. 0., Use 3p orbital, unoccupied.
3, 2, 0., 0., Use 3d orbital, unoccupied (polarization).
21., 0, 0, 0, 0, Normal run for scandium.
21., 0, 0, 1, 2, Compute spin energy.
21., 1, 0, 1, -1 Compute orbitals using new occupation defined by
one line; this will be Sc+2.
4, 0, -.1, -1. Remove one alpha, one beta electron from 4s.
21., 2, 0, 1, -1, Compute more orbitals using new occupation defined
by next 2 lines; this will be a 4s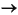 4p excited state.
4, 1, 1., 0. Use 4p with 1 alpha electron added.
4, 0, -1., -1. Use 4s with 1 alpha electron removed.
-1. End of input.
4p excited state.
4, 1, 1., 0. Use 4p with 1 alpha electron added.
4, 0, -1., -1. Use 4s with 1 alpha electron removed.
-1. End of input.
The formatted output of the DAtom utility appears in a file named outatom. The output for each atom begins with a reproduction of the input line. Next follows a line with the interpretation by the program. For example:
input as read: 1.,0,0,0,0, ! H interpreted as: 1.0 Hydrogen 0 0 0 0These are simply the values of the input variables described in the Input section above.
dist 1 2.86E-01 1 0 0.55 0.29 dist 16 3.39E-09 1 0 1.00 -0.09The warning "10 e trials exceeded" typically indicates that the level being calculated is unbound and that the corresponding orbital is not useful as a basis function. Such orbitals are excluded from the basis set.
When practical convergence is reached, a line is printed giving further information on the degree of convergence. The first number is the maximum difference in static potential between the last and the previous iteration (in Hartrees), followed by the radius of the maximum difference in Bohrs. The subsequent numbers give the charge and spin density differences with the radius:
dist vrs 1.39E-07 8.22 6.35E-09 2.81 4.92E-09 2.81The final part for each atomic calculation includes a summary of the atomic occupations, together with eigenvalues and accuracy estimates:
1s 2.00 -18.756782 -6.85E-09Ha -510.398eV 2s 2.00 -0.874078 -2.75E-09Ha -23.785eV 2p 4.00 -0.341238 -2.67E-09Ha -9.286eVOn supplementary basis function generation, information on the residual norm (after orthogonalization) and possible rejection of the basis function is displayed. For example, the C+2 ion output is:
input as read: 6.,1,0,1,-1, interpreted as: 6.0 Carbon 1 0 1 -1 n, L, delta occ 2 1 -2.000 0.000This indicates that two alpha electrons are removed from the 2p orbital. After convergence, the following output appears:
orthogonalized against n=1 0.999997 orthogonalized against n=2 0.001726 1s 2.00 -11.237952 4.37E-10Ha -305.803eV 3.13E-06 residual rejected as basisfunction, norm after orthogonalization too small orthogonalized against n=1 -0.001924 orthogonalized against n=2 0.984883 2s 2.00 -1.478535 7.79E-10Ha -40.233eV 3.00E-02 residual orthogonalized against n=2 0.954220 2p 0.00 -1.173406 8.16E-10Ha -31.930eV 8.95E-02 residualThis indicates that the 1s function of the ion is linearly correlated with the basis functions of the neutral atom and is rejected. The 2s and 2p functions are retained.
orthogonalized against n=1 0.999997 orthogonalized against n=2 0.001726 1s 2.00 -11.237952 4.37E-10Ha -305.803eV 3.13E-06 residual rejected as basisfunction, norm after orthogonalization too small orthogonalized against n=1 -0.001924 orthogonalized against n=2 0.984883 2s 2.00 -1.478535 7.79E-10Ha -40.233eV 3.00E-02 residual orthogonalized against n=2 0.954220 2p 0.00 -1.173406 8.16E-10Ha -31.930eV 8.95E-02 residualThe output ends with several lines on atomic energy integrals:
ion charge 8.881784E-16 total energy -37.434602Ha -1018.657eV sumei,eee,eze (Ha) -21.305706 35.243079 -87.496054 kinetic energy 37.176224Ha 1011.626eV exchange+correlation -4.736312Ha -128.883eV atom time 0.034 0.558The program then goes on to the calculation for the next atom.
The following sections of the dmol script can be customized:
# this section can be customized
# remove basis set file
/bin/ls ${job_name}.basis >& /dev/null
if ($status == 0) then
rm -f ${job_name}.basis
endif
# remove inatom file
/bin/ls ${job_name}.inatom >& /dev/null
if ($status == 0) then
rm -f ${job_name}.inatom
endif
# remove outatom file
/bin/ls ${job_name}.outatom >& /dev/null
if ($status == 0) then
rm -f ${job_name}.outatom
endif
The tables below begin with a line summarizing the basis set. First comes the atom name. This is followed by nbas=, which indicates its position in the .basis file. This should be equal to the atomic number of the atom, indicated by z=. The number of radial functions indicates how many atomic orbitals are available for use as basis sets for this atom. Finally, the spin energy (in Hartrees) appears. This is the difference in energy between a spin-restricted and spin-unrestricted atomic calculation.
The subsequent lines give information for each atomic orbital. The first two numbers give the principal and angular momentum quantum numbers (n and L). These are followed by the occupation of the atomic orbital. An occupation of zero indicates orbitals from supplementary calculations, that is, ionic or hydrogenic basis function calculations. Last comes the energy in both Hartrees and electron volts.
For example, for carbon the 1s, 2s, and 2p orbitals appear with occupations of 2.0 each. Next come a second 2s and 2p orbital--these were generated by an ionic calculation. Following this appears a 3d, 2p, and 1s orbital generated from a hydrogenic calculation using z = 5. Last comes a second set of 3d, 2p, and 1s orbitals, generated from a hydrogenic z = 7 calculation.
(Jump to below this list.)
Hydrogen nbas= 1 z= 1. 5 radial functions, spin energy= -0.033 n=1 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.233471 -6.3531 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.845000 -22.9936 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.211250 -5.7484 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -2.000000 -54.4228 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -8.000000 -217.6912 Helium nbas= 2 z= 2. 5 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.570425 -15.5221 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -2.000000 -54.4228 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.500000 -13.6057 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -2.000000 -54.4228 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -8.000000 -217.6912 Lithium nbas= 3 z= 3. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.009 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.878565 -51.1184 n=2 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.105540 -2.8719 n=2 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.239927 -6.5287 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.167949 -4.5701 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.388889 -37.7936 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -3.125000 -85.0356 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -12.500000 -340.1425 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.722222 -74.0755 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -6.124999 -166.6698 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -24.500000 -666.6792 Beryllium nbas= 4 z= 4. 10 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.856411 -104.9383 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.205744 -5.5986 n=2 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.501175 -13.6377 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.360797 -9.8178 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.388889 -37.7936 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -3.125000 -85.0356 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -12.500000 -340.1425 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.722222 -74.0755 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -6.124999 -166.6698 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -24.500000 -666.6792 Boron nbas= 5 z= 5. 11 radial functions, spin energy= -0.009 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -6.564347 -178.6250 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.344701 -9.3798 n=2 L=1 occ= 1.00 e= -0.136603 -3.7172 n=2 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.151191 -31.3255 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.937633 -25.5143 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.388889 -37.7936 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -3.125000 -85.0356 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -12.500000 -340.1425 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.722222 -74.0755 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -6.124999 -166.6698 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -24.500000 -666.6792 Carbon nbas= 6 z= 6. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.044 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -9.947718 -270.6913 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.500866 -13.6293 n=2 L=1 occ= 2.00 e= -0.199186 -5.4201 n=2 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.475702 -40.1559 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.170582 -31.8532 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.388889 -37.7936 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -3.125000 -85.0356 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -12.500000 -340.1425 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.722222 -74.0755 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -6.124999 -166.6698 Nitrogen nbas= 7 z= 7. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.112 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -14.011501 -381.2725 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.676151 -18.3990 n=2 L=1 occ= 3.00 e= -0.266297 -7.2463 n=2 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.795835 -48.8672 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.382823 -37.6286 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.388889 -37.7936 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -3.125000 -85.0356 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -12.500000 -340.1425 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.722222 -74.0755 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -6.124999 -166.6698 Oxygen nbas= 8 z= 8. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.054 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -18.758245 -510.4380 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.871362 -23.7110 n=2 L=1 occ= 4.00 e= -0.338381 -9.2078 n=2 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -2.130332 -57.9693 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.593734 -43.3677 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.388889 -37.7936 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -3.125000 -85.0356 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -12.500000 -340.1425 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.722222 -74.0755 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -6.124999 -166.6698 Fluorine nbas= 9 z= 9. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.015 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -24.189391 -658.2271 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.086859 -29.5749 n=2 L=1 occ= 5.00 e= -0.415606 -11.3092 n=2 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -2.481432 -67.5232 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.805649 -49.1342 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.388889 -37.7936 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -3.125000 -85.0356 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -12.500000 -340.1425 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.722222 -74.0755 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -6.124999 -166.6698 Neon nbas=10 z=10. 10 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -30.305855 -824.6646 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.322808 -35.9955 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.498034 -13.5522 n=2 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -3.266696 -88.8914 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -2.472214 -67.2724 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.388889 -37.7936 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -3.125000 -85.0356 n=1 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -12.500000 -340.1425 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.722222 -74.0755 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -6.124999 -166.6698 Sodium nbas=11 z=11. 9 radial functions, spin energy= -0.008 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -37.719977 -1026.4132 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.063402 -56.1481 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.060638 -28.8614 n=3 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.103416 -2.8141 n=2 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -3.237505 -88.0970 n=2 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -2.236742 -60.8649 n=3 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.626276 -17.0418 n=3 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.452324 -12.3084 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.260803 -7.0968 Magnesium nbas=12 z=12. 7 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -45.973167 -1250.9941 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.903746 -79.0150 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.718970 -46.7756 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.175427 -4.7736 n=3 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.657457 -17.8903 n=3 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.463094 -12.6014 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.254927 -6.9369 Aluminum nbas=13 z=13. 8 radial functions, spin energy= -0.006 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -55.156045 -1500.8730 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.934828 -107.0722 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.564019 -69.7705 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.286884 -7.8065 n=3 L=1 occ= 1.00 e= -0.102546 -2.7904 n=3 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.877774 -23.8855 n=3 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.639090 -17.3905 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.354504 -9.6466 Silicon nbas=14 z=14. 8 radial functions, spin energy= -0.025 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -65.184426 -1773.7592 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -5.075056 -138.0994 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -3.514939 -95.6464 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.398139 -10.8339 n=3 L=1 occ= 2.00 e= -0.153293 -4.1713 n=3 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.051059 -28.6008 n=3 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.759425 -20.6650 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.396362 -10.7856 Phosphorus nbas=15 z=15. 8 radial functions, spin energy= -0.060 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -76.061897 -2069.7504 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -6.329346 -172.2303 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -4.576617 -124.5361 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.512364 -13.9421 n=3 L=1 occ= 3.00 e= -0.206080 -5.6077 n=3 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.246546 -33.9203 n=3 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.896798 -24.4031 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.445449 -12.1213 Sulfur nbas= 1 z=16. 8 radial functions, spin energy= -0.028 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -87.789937 -2388.8868 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -7.699940 -209.5261 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -5.751258 -156.4997 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.630912 -17.1680 n=3 L=1 occ= 4.00 e= -0.261676 -7.1206 n=3 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.442798 -39.2605 n=3 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.032118 -28.0854 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.485455 -13.2099 Chlorine nbas= 2 z=17. 8 radial functions, spin energy= -0.007 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -100.369229 -2731.1869 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -9.187993 -250.0181 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -7.039983 -191.5678 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.754458 -20.5299 n=3 L=1 occ= 5.00 e= -0.320380 -8.7180 n=3 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.641864 -44.6774 n=3 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.167752 -31.7762 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.519598 -14.1390 Argon nbas= 3 z=18. 8 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -113.800134 -3096.6605 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -10.794173 -293.7245 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -8.443440 -229.7578 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.883384 -24.0381 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.382330 -10.4037 n=3 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.844776 -50.1989 n=3 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.304742 -35.5038 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.549139 -14.9428 Potassium nbas= 4 z=19. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.005 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -128.414963 -3494.3504 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -12.839007 -349.3673 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -10.283857 -279.8381 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.281902 -34.8823 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.693782 -18.8788 n=4 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.088818 -2.4169 n=3 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.443661 -39.2840 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.504490 -13.7279 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.372679 -10.1411 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.574752 -15.6398 Calcium nbas= 5 z=20. 9 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -143.935182 -3916.6772 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -15.046906 -409.4473 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -12.285377 -334.3023 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.706331 -46.4317 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.030573 -28.0433 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.141411 -3.8480 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.526691 -14.3320 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.385494 -10.4898 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.596854 -16.2412 Scandium nbas= 6 z=21. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.006 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -160.184109 -4358.8332 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -17.206464 -468.2119 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -14.240006 -387.4904 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.988378 -54.1066 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.233165 -33.5562 n=3 L=2 occ= 1.00 e= -0.131080 -3.5669 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.156478 -4.2580 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.670718 -18.2512 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.578249 -15.7350 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.425974 -11.5914 Titanium nbas= 7 z=22. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.026 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -177.276644 -4823.9450 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -19.457900 -529.4766 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -16.285339 -443.1468 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.258006 -61.4435 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.422947 -38.7204 n=3 L=2 occ= 2.00 e= -0.170010 -4.6262 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.167106 -4.5472 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.930320 -25.3153 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.703882 -19.1536 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.527973 -14.3669 Vanadium nbas= 8 z=23. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.063 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -195.224015 -5312.3180 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -21.815345 -593.6260 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -18.435188 -501.6472 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.526903 -68.7606 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.610515 -43.8244 n=3 L=2 occ= 3.00 e= -0.204634 -5.5684 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.175968 -4.7883 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.001024 -27.2393 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.736999 -20.0548 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.547805 -14.9065 Chromium nbas= 9 z=24. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.188 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -213.881192 -5820.0058 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -24.113456 -656.1608 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -20.526272 -558.5485 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.649084 -72.0853 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.654229 -45.0139 n=3 L=2 occ= 5.00 e= -0.118123 -3.2143 n=4 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.150445 -4.0938 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.855979 -23.2924 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.682052 -18.5596 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.492022 -13.3886 Manganese nbas=10 z=25. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.195 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -233.696912 -6359.2192 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -26.866644 -731.0789 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -23.066295 -627.6661 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.076636 -83.7196 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.991449 -54.1901 n=3 L=2 occ= 5.00 e= -0.266540 -7.2529 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.191136 -5.2011 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.132458 -30.8158 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.797824 -21.7099 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.582294 -15.8450 Iron nbas= 1 z=26. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.130 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -254.225504 -6917.8309 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -29.564858 -804.5011 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -25.551764 -695.2992 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.360620 -91.4472 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.187522 -59.5255 n=3 L=2 occ= 6.00 e= -0.295049 -8.0287 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.197978 -5.3872 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.194380 -32.5007 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.826288 -22.4844 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.597572 -16.2608 Cobalt nbas= 2 z=27. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.076 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -275.616638 -7499.9135 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -32.379756 -881.0984 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -28.152093 -766.0577 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.651810 -99.3709 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.388284 -64.9885 n=3 L=2 occ= 7.00 e= -0.322368 -8.7721 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.204497 -5.5646 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.254294 -34.1311 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.853764 -23.2321 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.611803 -16.6480 Nickel nbas= 3 z=28. 10 radial functions, spin energy= -0.035 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -297.870824 -8105.4810 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -35.312108 -960.8918 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -30.868024 -839.9620 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.950716 -107.5045 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.594156 -70.5906 n=3 L=2 occ= 8.00 e= -0.348698 -9.4886 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.210764 -5.7352 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.312475 -35.7143 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.880407 -23.9571 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.625121 -17.0104 Zinc nbas= 4 z=30. 10 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -344.969755 -9387.1087 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -41.531318 -1130.1251 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -36.648760 -997.2639 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -4.573040 -124.4388 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -3.022362 -82.2427 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.398944 -10.8558 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.222725 -6.0606 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.424445 -38.7611 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.931630 -25.3510 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.649415 -17.6715 Gallium nbas= 5 z=31. 12 radial functions, spin energy= -0.005 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -370.170639 -10072.8599 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -45.200865 -1229.9786 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -40.093336 -1090.9956 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -5.241644 -142.6325 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -3.584666 -97.5438 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.736205 -20.0332 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.328019 -8.9259 n=4 L=1 occ= 1.00 e= -0.101635 -2.7656 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.787856 -48.6501 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.045637 -28.4532 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.727629 -19.7998 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.333561 -9.0767 Germanium nbas= 6 z=32. 12 radial functions, spin energy= -0.023 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -396.292991 -10783.6856 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -49.055278 -1334.8626 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -43.720124 -1189.6856 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -5.961470 -162.2199 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -4.194820 -114.1469 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.117316 -30.4037 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.426523 -11.6063 n=4 L=1 occ= 2.00 e= -0.149882 -4.0785 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.252517 -61.2941 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.190853 -32.4048 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.830249 -22.5922 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.373933 -10.1752 Arsenic nbas= 7 z=33. 12 radial functions, spin energy= -0.052 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -423.336659 -11519.5815 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -53.093081 -1444.7369 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -47.527864 -1293.2995 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -6.730754 -183.1532 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -4.851724 -132.0222 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.542769 -41.9809 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.523670 -14.2498 n=4 L=1 occ= 3.00 e= -0.197497 -5.3742 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -2.760238 -75.1099 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.335131 -36.3308 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.929989 -25.3063 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.406514 -11.0618 Selenium nbas= 8 z=34. 12 radial functions, spin energy= -0.023 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -451.300260 -12280.5101 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -57.311945 -1559.5380 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -51.514384 -1401.7783 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -7.547186 -205.3695 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -5.553516 -151.1189 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -2.011395 -54.7329 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.621248 -16.9050 n=4 L=1 occ= 4.00 e= -0.245807 -6.6887 n=3 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -3.309507 -90.0563 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.479611 -40.2623 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.028863 -27.9968 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.435355 -11.8466 Bromine nbas= 1 z=35. 11 radial functions, spin energy= -0.006 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -480.182645 -13066.4402 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -61.710018 -1679.2158 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -55.677957 -1515.0749 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -8.409058 -228.8222 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -6.298804 -171.3992 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -2.522114 -68.6303 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.720067 -19.5940 n=4 L=1 occ= 5.00 e= -0.295335 -8.0365 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.624923 -44.2164 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.127743 -30.6875 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.461782 -12.5657 Krypton nbas= 2 z=36. 11 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -509.982993 -13877.3492 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -66.285950 -1803.7332 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -60.017325 -1633.1552 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -9.315193 -253.4794 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -7.086634 -192.8372 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -3.074114 -83.6509 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.820575 -22.3290 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.346341 -9.4244 n=4 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.771485 -48.2046 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.227130 -33.3919 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.486464 -13.2374 Rubidium nbas= 3 z=37. 13 radial functions, spin energy= -0.005 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -540.957129 -14720.1987 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -71.291208 -1939.9333 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -64.784684 -1762.8817 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -10.513870 -286.0971 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -8.165424 -222.1926 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -3.915523 -106.5468 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.135059 -30.8865 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.592178 -16.1140 n=5 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.085380 -2.3233 n=4 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.243735 -33.8438 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.472250 -12.8506 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.480123 -13.0648 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.344356 -9.3704 Strontium nbas= 4 z=38. 12 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -572.870177 -15588.5973 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -76.491822 -2081.4493 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -69.745940 -1897.8844 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -11.771588 -320.3213 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -9.301864 -253.1167 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -4.813506 -130.9822 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.455319 -39.6013 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.844489 -22.9797 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.131793 -3.5863 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.489267 -13.3136 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.502260 -13.6672 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.354931 -9.6582 Yttrium nbas= 5 z=39. 13 radial functions, spin energy= -0.005 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -605.631987 -16480.0919 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -81.789101 -2225.5956 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -74.803199 -2035.4995 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -12.992219 -353.5364 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -10.399926 -282.9965 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -5.671507 -154.3296 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.697125 -46.1811 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.024490 -27.8778 n=4 L=2 occ= 1.00 e= -0.108692 -2.9577 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.150727 -4.1015 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.581909 -15.8346 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.544274 -14.8104 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.400601 -10.9009 Zirconium nbas= 6 z=40. 13 radial functions, spin energy= -0.019 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -639.292243 -17396.0344 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -87.237058 -2373.8421 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -80.010039 -2177.1849 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -14.230433 -387.2300 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -11.514413 -313.3233 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -6.544651 -178.0891 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.918971 -52.2179 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.186595 -32.2889 n=4 L=2 occ= 2.00 e= -0.150674 -4.1000 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.162391 -4.4189 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.751595 -20.4519 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.640507 -17.4291 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.478225 -13.0132 Niobium nbas= 7 z=41. 13 radial functions, spin energy= -0.099 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -673.762537 -18334.0193 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -92.740856 -2523.6082 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -85.272170 -2320.3748 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -15.393727 -418.8848 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -12.552851 -341.5806 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -7.339846 -199.7275 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.036691 -55.4212 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.250046 -34.0155 n=4 L=2 occ= 4.00 e= -0.125252 -3.4083 n=5 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.144272 -3.9258 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.720210 -19.5979 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.613400 -16.6915 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.448199 -12.1961 Molybdenum nbas= 8 z=42. 13 radial functions, spin energy= -0.149 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -709.232123 -19299.1962 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -98.503634 -2680.4214 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -90.791536 -2470.5644 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -16.681545 -453.9281 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -13.714804 -373.1990 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -8.257729 -224.7043 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.234822 -60.8126 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.390045 -37.8251 n=4 L=2 occ= 5.00 e= -0.153347 -4.1728 n=5 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.147880 -4.0240 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.784451 -21.3460 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.640138 -17.4191 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.465171 -12.6580 Technetium nbas= 1 z=43. 13 radial functions, spin energy= -0.137 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -745.742030 -20292.6818 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -104.567503 -2845.4277 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -96.610205 -2628.8985 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -18.135303 -493.4869 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -15.041732 -409.3065 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -9.339869 -254.1509 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.550710 -69.4084 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.643225 -44.7145 n=4 L=2 occ= 5.00 e= -0.270263 -7.3542 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.183636 -4.9970 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.971592 -26.4384 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.726241 -19.7620 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.532581 -14.4923 Ruthenium nbas= 1 z=44. 13 radial functions, spin energy= -0.063 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -782.918627 -21304.3089 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -110.536047 -3007.8402 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -102.333641 -2784.6413 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -19.366689 -526.9947 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -16.145209 -439.3337 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -10.195676 -277.4386 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.628359 -71.5213 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.667543 -45.3762 n=4 L=2 occ= 7.00 e= -0.210375 -5.7246 n=5 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.152833 -4.1588 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.907759 -24.7014 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.685222 -18.6458 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.492123 -13.3914 Rhodium nbas= 2 z=45. 13 radial functions, spin energy= -0.034 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -821.136778 -22344.2781 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -116.806943 -3178.4800 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -108.357657 -2948.5631 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -20.765600 -565.0610 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -17.415289 -473.8943 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -11.217258 -305.2372 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.825500 -76.8858 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.806448 -49.1560 n=4 L=2 occ= 8.00 e= -0.239422 -6.5150 n=5 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.154623 -4.2075 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.967719 -26.3330 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.704830 -19.1794 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.503174 -13.6921 Palladium nbas= 3 z=46. 13 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -860.134915 -23405.4719 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -123.105069 -3349.8608 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -114.408277 -3113.2089 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -22.060893 -600.3077 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -18.580786 -505.6091 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -12.132204 -330.1342 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.889167 -78.6183 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.815205 -49.3943 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.160770 -4.3748 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.113587 -3.0909 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.026922 -27.9440 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.722994 -19.6737 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.513032 -13.9603 Silver nbas= 4 z=47. 13 radial functions, spin energy= -0.006 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -900.324583 -24499.0888 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -129.859799 -3533.6664 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -120.913341 -3290.2208 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -23.678432 -644.3232 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -20.067617 -546.0679 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -13.367811 -363.7568 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.223085 -87.7046 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.086591 -56.7791 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.298705 -8.1282 n=5 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.157407 -4.2833 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.085556 -29.5395 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.739964 -20.1355 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.521899 -14.2016 Cadmium nbas= 5 z=48. 13 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -941.476653 -25618.8941 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -136.832484 -3723.4029 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -127.635112 -3473.1296 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -25.379904 -690.6226 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -21.637509 -588.7868 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -14.685262 -399.6065 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.596065 -97.8539 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.395250 -65.1781 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.470530 -12.8038 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.204227 -5.5573 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.314586 -35.7717 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.830549 -22.6004 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.592423 -16.1207 Indium nbas= 6 z=49. 15 radial functions, spin energy= -0.005 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -983.647457 -26766.4206 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -144.078353 -3920.5731 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -134.628839 -3663.4387 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -27.220599 -740.7105 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -23.345767 -635.2709 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -16.139837 -439.1875 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -4.062637 -110.5500 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.795823 -76.0782 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.730485 -19.8775 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.290498 -7.9049 n=5 L=1 occ= 1.00 e= -0.101783 -2.7697 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.566590 -42.6291 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.917025 -24.9535 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.654451 -17.8085 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.320794 -8.7292 Tin nbas= 7 z=50. 15 radial functions, spin energy= -0.019 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1026.762181 -27939.6324 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -151.523989 -4123.1793 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -141.821087 -3859.1498 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -29.125968 -792.5583 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -25.117903 -683.4932 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -17.657292 -480.4796 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -4.546334 -123.7121 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -3.211989 -87.4027 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.004957 -27.3463 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.369349 -10.0505 n=5 L=1 occ= 2.00 e= -0.144449 -3.9307 n=4 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.883282 -51.2467 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.028482 -27.9864 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.736392 -20.0383 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.358988 -9.7686 Antimony nbas= 2 z=51. 14 radial functions, spin energy= -0.043 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1070.823511 -29138.6027 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -159.171743 -4331.2854 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -149.214268 -4060.3285 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -31.098243 -846.2266 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -26.956175 -733.5151 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -19.239914 -523.5449 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -5.049641 -137.4078 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -3.646571 -99.2283 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.297346 -35.3026 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.445605 -12.1255 n=5 L=1 occ= 3.00 e= -0.185623 -5.0511 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.137859 -30.9627 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.814990 -22.1770 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.390641 -10.6299 Tellurium nbas= 3 z=52. 14 radial functions, spin energy= -0.019 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1115.831836 -30363.3421 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -167.021777 -4544.8957 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -156.808582 -4266.9804 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -33.137488 -901.7173 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -28.860676 -785.3393 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -20.887822 -568.3868 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -5.572848 -151.6450 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -4.100077 -111.5688 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.608391 -43.7666 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.520998 -14.1771 n=5 L=1 occ= 4.00 e= -0.226593 -6.1659 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.246286 -33.9132 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.892100 -24.2753 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.419334 -11.4107 Iodine nbas= 4 z=53. 14 radial functions, spin energy= -0.005 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1161.787070 -31613.8482 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -175.073808 -4764.0027 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -164.603791 -4479.0990 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -35.243356 -959.0209 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -30.831086 -838.9569 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -22.600718 -614.9971 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -6.115816 -166.4199 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -4.572515 -124.4245 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.938192 -52.7409 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.596341 -16.2273 n=5 L=1 occ= 5.00 e= -0.267904 -7.2900 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.354372 -36.8544 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.968537 -26.3552 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.446252 -12.1432 Xenon nbas= 5 z=54. 14 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1208.689018 -32890.1156 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -183.327503 -4988.5973 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -172.599587 -4696.6757 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -37.415461 -1018.1269 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -32.867037 -894.3580 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -24.378260 -663.3665 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -6.678347 -181.7271 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -5.063795 -137.7929 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -2.286682 -62.2238 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.672089 -18.2885 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.309835 -8.4310 n=5 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.462515 -39.7971 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.044768 -28.4296 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.471988 -12.8435 Cesium nbas= 1 z=55. 16 radial functions, spin energy= -0.004 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1256.738836 -34197.6183 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -191.981900 -5224.0955 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -180.995367 -4925.1366 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -39.851609 -1084.4179 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -35.166433 -956.9277 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -26.418446 -718.8828 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -7.455990 -202.8879 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -5.769335 -156.9917 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -2.848420 -77.5095 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.915838 -24.9212 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.504917 -13.7395 n=6 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.078710 -2.1418 n=5 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -1.059595 -28.8331 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.422431 -11.4949 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.472320 -12.8525 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.315641 -8.5890 Barium nbas= 2 z=56. 15 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1305.743290 -35531.0979 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -200.844457 -5465.2581 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -189.598492 -5159.2397 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -42.359446 -1152.6597 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -37.536928 -1021.4322 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -28.528970 -776.3131 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -8.257072 -224.6865 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -6.497617 -176.8092 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -3.432463 -93.4021 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.157164 -31.4880 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.698605 -19.0100 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.118968 -3.2373 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.436628 -11.8813 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.496858 -13.5202 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.325036 -8.8447 Lanthanum nbas= 1 z=57. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.004 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1355.622480 -36888.3803 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -209.831165 -5709.7989 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -198.325251 -5396.7070 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -44.856294 -1220.6024 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -39.895833 -1085.6213 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -30.626733 -833.3962 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -9.000553 -244.9176 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -7.167715 -195.0435 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -3.958031 -107.7035 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.324939 -36.0534 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.824494 -22.4356 n=5 L=2 occ= 1.00 e= -0.141088 -3.8392 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.132234 -3.5983 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.563494 -15.3335 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.479415 -13.0456 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.360899 -9.8206 n=4 L=3 occ= 0.00 e= -0.753946 -20.5159 Cerium nbas= 2 z=58. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.022 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1405.895474 -38256.3786 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -218.406482 -5943.1453 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -206.652214 -5623.2953 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -46.717445 -1271.2469 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -41.622070 -1132.5946 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -32.100960 -873.5119 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -9.149870 -248.9807 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -7.253894 -197.3886 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -3.926262 -106.8391 n=4 L=3 occ= 2.00 e= -0.125991 -3.4284 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.255017 -34.1508 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.755746 -20.5649 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.123017 -3.3475 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.100805 -2.7430 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.452214 -12.3054 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.335314 -9.1244 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.511067 -13.9068 Praseodymium nbas= 3 z=59. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.051 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1457.338103 -39656.2044 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -227.426377 -6188.5892 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -215.418319 -5861.8332 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -48.925003 -1331.3176 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -43.692539 -1188.9350 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -33.914033 -922.8482 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -9.577457 -260.6160 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -7.613098 -207.1630 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -4.154251 -113.0430 n=4 L=3 occ= 3.00 e= -0.155143 -4.2216 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.296111 -35.2690 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.778045 -21.1717 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.124466 -3.3869 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.098947 -2.6925 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.458194 -12.4681 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.338771 -9.2184 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.514801 -14.0085 Neodymium nbas= 4 z=60. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.095 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1509.698990 -41081.0172 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -236.613583 -6438.5859 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -224.351823 -6104.9263 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -51.161271 -1392.1696 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -45.791207 -1246.0427 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -35.754553 -972.9313 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -10.000902 -272.1385 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -7.967808 -216.8152 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -4.377050 -119.1057 n=4 L=3 occ= 4.00 e= -0.179513 -4.8848 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.334940 -36.3256 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.798502 -21.7283 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.125797 -3.4231 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.096447 -2.6245 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.463674 -12.6172 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.341813 -9.3012 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.517328 -14.0772 Promethium nbas= 5 z=61. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.152 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1562.980317 -42530.8765 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -245.970558 -6693.2023 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -233.455119 -6352.6397 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -53.429319 -1453.8864 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -47.921120 -1304.0006 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -37.625472 -1023.8416 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -10.422767 -283.6180 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -8.320482 -226.4119 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -4.596847 -125.0866 n=4 L=3 occ= 5.00 e= -0.200164 -5.4467 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.372271 -37.3414 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.817701 -22.2508 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.127054 -3.4573 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.093510 -2.5445 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.468830 -12.7575 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.344594 -9.3769 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.518972 -14.1219 Samarium nbas= 1 z=62. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.225 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1617.183462 -44005.8198 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -255.498857 -6952.4806 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -242.729731 -6605.0149 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -55.731140 -1516.5221 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -50.084244 -1362.8622 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -39.528695 -1075.6310 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -10.844678 -295.0988 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -8.672671 -235.9955 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -4.815003 -131.0230 n=4 L=3 occ= 6.00 e= -0.217764 -5.9257 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.408558 -38.3288 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.835985 -22.7483 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.128260 -3.4901 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.090253 -2.4559 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.473760 -12.8917 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.347195 -9.4476 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.519934 -14.1481 Europium nbas= 2 z=63. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.312 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1672.309357 -45505.8723 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -265.199544 -7216.4498 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -252.176704 -6862.0802 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -58.068134 -1580.1150 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -52.281971 -1422.6654 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -41.465558 -1128.3357 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -11.267758 -306.6114 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -9.025440 -245.5948 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -5.032446 -136.9399 n=4 L=3 occ= 7.00 e= -0.232778 -6.3342 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.444094 -39.2958 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.853574 -23.2269 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.129427 -3.5219 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.086756 -2.3608 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.478524 -13.0213 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.349663 -9.5148 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.520347 -14.1594 Gadolinium nbas= 3 z=64. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.362 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1728.625231 -47038.3059 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -275.363139 -7493.0154 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -262.081617 -7131.6067 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -60.764410 -1653.4844 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -54.836899 -1492.1886 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -43.754594 -1190.6236 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -11.986495 -326.1693 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -9.669845 -263.1300 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -5.531860 -150.5296 n=4 L=3 occ= 7.00 e= -0.489013 -13.3067 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.608481 -43.7690 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.978744 -26.6330 n=5 L=2 occ= 1.00 e= -0.127223 -3.4619 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.143627 -3.9083 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.582884 -15.8611 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.520470 -14.1627 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.384979 -10.4758 Terbium nbas= 4 z=65. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.166 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1785.331978 -48581.3756 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -285.121021 -7758.5410 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -271.590589 -7390.3591 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -62.851567 -1710.2789 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -56.785090 -1545.2016 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -45.443904 -1236.5921 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -12.120497 -329.8157 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -9.735620 -264.9198 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -5.467690 -148.7835 n=4 L=3 occ= 9.00 e= -0.256316 -6.9747 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.513676 -41.1892 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.887229 -24.1428 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.131678 -3.5831 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.079251 -2.1565 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.487691 -13.2707 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.354315 -9.6414 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.519878 -14.1466 Dysprosium nbas= 5 z=66. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.108 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1843.229626 -50156.8514 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -295.342867 -8036.6917 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -281.558533 -7661.6008 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -65.299446 -1776.8891 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -59.091907 -1607.9733 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -47.486742 -1292.1806 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -12.551263 -341.5374 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -10.094071 -274.6738 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -5.686382 -154.7344 n=4 L=3 occ=10.00 e= -0.265307 -7.2194 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.547984 -42.1228 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.903489 -24.5852 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.132770 -3.6129 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.075319 -2.0495 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.492140 -13.3918 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.356533 -9.7018 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.519120 -14.1260 Holmium nbas= 1 z=67. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.062 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1902.051947 -51757.4889 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -305.739302 -8319.5933 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -291.700996 -7937.5913 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -67.785495 -1844.5380 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -61.436276 -1671.7669 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -49.566039 -1348.7611 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -12.985510 -353.3539 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -10.455283 -284.5029 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -5.906226 -160.7166 n=4 L=3 occ=11.00 e= -0.272682 -7.4201 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.582096 -43.0510 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.919462 -25.0199 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.133845 -3.6421 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.071308 -1.9404 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.496522 -13.5110 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.358697 -9.7606 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.518074 -14.0975 Erbium nbas= 2 z=68. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.028 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1961.799213 -53383.2954 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -316.310642 -8607.2542 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -302.018270 -8218.3388 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -70.310144 -1913.2372 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -63.818627 -1736.5939 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -51.682192 -1406.3446 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -13.423560 -365.2738 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -10.819552 -294.4151 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -6.127475 -166.7372 n=4 L=3 occ=12.00 e= -0.278582 -7.5806 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.616082 -43.9758 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.935201 -25.4481 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.134906 -3.6710 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.067242 -1.8298 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.500846 -13.6287 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.360813 -9.8182 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.516775 -14.0622 Thulium nbas= 3 z=69. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.007 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2022.471649 -55034.2771 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -327.057128 -8899.6811 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -312.510609 -8503.8500 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -72.873754 -1982.9966 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -66.239305 -1802.4640 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -53.835538 -1464.9402 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -13.865678 -377.3045 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -11.187129 -304.4174 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -6.350340 -172.8016 n=4 L=3 occ=13.00 e= -0.283125 -7.7042 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.649998 -44.8988 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.950748 -25.8712 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.135953 -3.6995 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.063144 -1.7182 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.505121 -13.7450 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.362889 -9.8747 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.515254 -14.0208 Ytterbium nbas= 4 z=70. 17 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2084.069429 -56710.4387 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -337.978981 -9196.8799 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -323.178217 -8794.1305 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -75.476630 -2053.8245 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -68.698621 -1869.3854 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -56.026360 -1524.5555 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -14.312090 -389.4520 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -11.558222 -314.5154 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -6.574997 -178.9149 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -0.286414 -7.7937 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.683895 -45.8211 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.966137 -26.2899 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.136990 -3.7277 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.059032 -1.6063 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.509356 -13.8603 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.364932 -9.9303 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.513535 -13.9740 Lutetium nbas= 5 z=71. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.004 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2146.885392 -58419.7488 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -349.390496 -9507.4032 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -334.330896 -9097.6105 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -78.462393 -2135.0713 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -71.538740 -1946.6690 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -58.593023 -1594.3980 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -15.083380 -410.4398 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -12.250875 -333.3634 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -7.113396 -193.5654 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -0.568098 -15.4587 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.872092 -50.9422 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.111987 -30.2587 n=5 L=2 occ= 1.00 e= -0.103690 -2.8215 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.155112 -4.2208 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.581940 -15.8354 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.557046 -15.1580 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.405476 -11.0336 Hafnium nbas= 3 z=72. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.018 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2210.652025 -60154.9279 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -361.006524 -9823.4915 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -345.687013 -9406.6263 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -81.522802 -2218.3493 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -74.452609 -2025.9594 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -61.231481 -1666.1941 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -15.883632 -432.2158 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -12.971176 -352.9638 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -7.676666 -208.8928 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -0.871573 -23.7167 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.049831 -55.7788 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.246434 -33.9172 n=5 L=2 occ= 2.00 e= -0.143808 -3.9132 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.166465 -4.5297 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.645478 -17.5643 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.590847 -16.0778 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.429680 -11.6922 Tantalum nbas= 4 z=73. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.043 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2275.371418 -61916.0329 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -372.828723 -10145.1901 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -357.248320 -9721.2256 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -84.658456 -2303.6748 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -77.440892 -2107.2748 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -63.942558 -1739.9663 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -16.713341 -454.7933 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -13.719772 -373.3341 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -8.265875 -224.9260 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -1.199343 -32.6358 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.223809 -60.5129 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.376520 -37.4570 n=5 L=2 occ= 3.00 e= -0.182466 -4.9652 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.174813 -4.7569 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.706173 -19.2159 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.618607 -16.8332 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.448304 -12.1990 Tungsten nbas= 5 z=74. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.078 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2341.042923 -63703.0463 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -384.856152 -10472.4732 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -369.013958 -10041.3850 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -87.867777 -2391.0049 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -80.502046 -2190.5731 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -66.724823 -1815.6756 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -17.570800 -478.1260 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -14.495059 -394.4308 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -8.879721 -241.6296 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -1.550831 -42.2003 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.396019 -65.1990 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.504444 -40.9380 n=5 L=2 occ= 4.00 e= -0.220606 -6.0030 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.181412 -4.9365 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.764886 -20.8136 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.642446 -17.4818 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.463583 -12.6147 Rhenium nbas= 1 z=75. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.124 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2407.665605 -65515.9425 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -397.087699 -10805.3107 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -380.982852 -10367.0753 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -91.149178 -2480.2964 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -83.634521 -2275.8121 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -69.576798 -1893.2818 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -18.454328 -502.1680 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -15.295450 -416.2106 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -9.516843 -258.9666 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -1.925075 -52.3840 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.567348 -69.8611 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.631212 -44.3875 n=5 L=2 occ= 5.00 e= -0.258641 -7.0380 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.186858 -5.0847 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.822178 -22.3726 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.663456 -18.0536 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.476550 -12.9676 Osmium nbas= 2 z=76. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.080 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2475.238647 -67354.6993 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -409.522391 -11143.6760 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -393.154062 -10698.2709 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -94.501307 -2571.5125 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -86.836984 -2362.9556 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -72.497221 -1972.7506 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -19.362530 -526.8815 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -16.119622 -438.6374 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -10.176110 -276.9062 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -2.321169 -63.1623 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.738292 -74.5128 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.757387 -47.8210 n=5 L=2 occ= 6.00 e= -0.296794 -8.0762 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.191488 -5.2106 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.878439 -23.9036 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.682307 -18.5665 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.487795 -13.2736 Iridium nbas= 3 z=77. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.045 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2543.761381 -69219.2985 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -422.159418 -11487.5471 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -405.526818 -11034.9509 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -97.923064 -2664.6233 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -90.108365 -2451.9744 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -75.485066 -2054.0540 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -20.294293 -552.2360 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -16.966528 -461.6829 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -10.856622 -295.4238 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -2.738334 -74.5139 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.909173 -79.1627 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.883329 -51.2480 n=5 L=2 occ= 7.00 e= -0.335192 -9.1210 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.195510 -5.3201 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.933949 -25.4141 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.699443 -19.0328 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.497696 -13.5430 Platinum nbas= 4 z=78. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.014 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2613.096567 -71106.0057 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -434.857994 -11833.0931 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -417.960510 -11373.2890 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -101.274850 -2755.8301 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -93.309043 -2539.0693 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -78.400311 -2133.3819 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -21.110652 -574.4503 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -17.697241 -481.5666 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -11.419504 -310.7406 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -3.038043 -82.6694 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2.950523 -80.2879 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -1.884233 -51.2726 n=5 L=2 occ= 9.00 e= -0.273635 -7.4460 n=6 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.161306 -4.3894 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.988916 -26.9098 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.715181 -19.4611 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.506511 -13.7829 Gold nbas= 5 z=79. 17 radial functions, spin energy= -0.006 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2683.508280 -73022.0067 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -447.888968 -12187.6841 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -430.725683 -11720.6472 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -104.824497 -2852.4209 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -96.706931 -2631.5306 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -81.511793 -2218.0497 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -22.078359 -600.7830 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -18.578594 -505.5495 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -12.131844 -330.1244 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -3.486818 -94.8812 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.113933 -84.7345 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.002470 -54.4900 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.304740 -8.2924 n=6 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.162332 -4.4173 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.043500 -28.3951 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.729753 -19.8576 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.514425 -13.9982 Mercury nbas= 1 z=80. 17 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2755.022683 -74968.0135 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -461.278637 -12552.0357 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -443.848663 -12077.7418 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -108.597904 -2955.1006 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -100.327964 -2730.0640 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -84.845538 -2308.7655 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -23.222925 -631.9282 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -19.636128 -534.3265 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -13.019254 -354.2721 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -4.110289 -111.8467 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.423485 -93.1578 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.261949 -61.5508 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.452555 -12.3146 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.205136 -5.5820 n=5 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -1.097825 -29.8733 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.743335 -20.2272 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.521578 -14.1929 Thallium nbas= 2 z=81. 18 radial functions, spin energy= -0.004 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2827.569458 -76942.1125 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -474.953376 -12924.1444 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -457.255962 -12442.5731 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -112.522170 -3061.8853 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -104.099231 -2832.6854 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -88.328353 -2403.5378 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -24.471523 -665.9043 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -20.797024 -565.9160 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -14.008889 -381.2014 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -4.835752 -131.5876 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3.811516 -103.7167 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.598707 -70.7144 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.674552 -18.3555 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.285022 -7.7558 n=6 L=1 occ= 1.00 e= -0.101507 -2.7621 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.822215 -22.3736 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.583022 -15.8649 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.287423 -7.8212 Lead nbas= 3 z=82. 18 radial functions, spin energy= -0.018 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2901.078124 -78942.3859 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -488.843345 -13302.1099 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -470.877782 -12813.2418 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -116.526846 -3170.8582 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -107.950330 -2937.4792 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -91.889984 -2500.4548 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -25.753345 -700.7845 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -21.990509 -598.3925 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -15.030072 -408.9892 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -5.592541 -152.1808 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -4.206804 -114.4730 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -2.941634 -80.0460 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -0.902404 -24.5557 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.357188 -9.7196 n=6 L=1 occ= 2.00 e= -0.141830 -3.8594 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.897368 -24.4186 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.637179 -17.3385 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.311108 -8.4657 Bismuth nbas= 1 z=83. 18 radial functions, spin energy= -0.039 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -2975.551026 -80968.8976 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -502.950772 -13685.9927 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -484.716359 -13189.8088 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -120.613998 -3282.0753 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -111.883337 -3044.5018 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -95.532544 -2599.5739 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -27.070360 -736.6223 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -23.218589 -631.8102 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -16.084868 -437.6917 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -6.382759 -173.6838 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -4.611945 -125.4975 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -3.293614 -89.6238 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.139423 -31.0053 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.426132 -11.5956 n=6 L=1 occ= 3.00 e= -0.180196 -4.9034 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.996867 -27.1261 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.710885 -19.3442 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.346791 -9.4367 Polonium nbas= 2 z=84. 18 radial functions, spin energy= -0.017 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3050.988486 -83021.6562 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -517.275868 -14075.7985 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -498.771926 -13572.2804 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -124.783688 -3395.5384 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -115.898328 -3153.7553 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -99.256142 -2700.8982 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -28.422565 -773.4177 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -24.481285 -666.1700 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -17.173365 -467.3112 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -7.206520 -196.0995 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -5.027462 -136.8043 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -3.655360 -99.4674 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.386477 -37.7280 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.493532 -13.4297 n=6 L=1 occ= 4.00 e= -0.217887 -5.9290 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.093470 -29.7548 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.780709 -21.2442 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.375883 -10.2283 Astatine nbas= 3 z=85. 18 radial functions, spin energy= -0.004 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3127.390351 -85100.6576 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -531.818380 -14471.5206 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -513.044258 -13960.6505 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -129.035553 -3511.2375 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -119.994963 -3265.2305 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -103.060458 -2804.4189 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -29.809546 -811.1594 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -25.778216 -701.4612 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -18.295226 -497.8387 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -8.063510 -219.4194 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -5.453403 -148.3947 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -4.027040 -109.5814 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.643780 -44.7295 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.560194 -15.2437 n=6 L=1 occ= 5.00 e= -0.255452 -6.9512 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.188312 -32.3356 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.848505 -23.0890 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.402045 -10.9402 Radon nbas= 4 z=86. 18 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3204.756377 -87205.8952 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -546.577994 -14873.1503 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -527.533042 -14354.9106 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -133.369162 -3629.1611 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -124.172812 -3378.9156 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -106.945098 -2910.1254 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -31.230841 -849.8348 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -27.108940 -737.6721 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -19.450066 -529.2634 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -8.953353 -243.6332 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -5.889706 -160.2671 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -4.408682 -119.9664 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -1.911356 -52.0107 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.626578 -17.0501 n=6 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.293179 -7.9778 n=6 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -1.282024 -34.8857 n=6 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.915097 -24.9011 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.426460 -11.6046 Francium nbas= 5 z=87. 19 radial functions, spin energy= -0.004 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3283.263512 -89342.1839 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -561.730515 -15285.4715 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -542.414284 -14759.8499 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -137.959674 -3754.0753 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -128.607110 -3499.5790 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -111.085341 -3022.7872 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -32.861075 -894.1957 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -28.648105 -779.5549 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -20.812558 -566.3387 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -10.050708 -273.4938 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -6.509563 -177.1343 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -4.973279 -135.3299 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -2.361039 -64.2472 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.841877 -22.9086 n=6 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.466214 -12.6863 n=7 L=0 occ= 1.00 e= -0.076191 -2.0733 n=7 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.190766 -5.1910 n=7 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.119472 -3.2510 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.176965 -4.8155 Radium nbas= 1 z=88. 19 radial functions, spin energy= 0.000 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3362.736662 -91504.7593 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -577.101258 -15703.7309 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -557.513247 -15170.7138 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -142.632453 -3881.2282 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -133.123211 -3622.4684 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -115.306583 -3137.6531 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -34.525675 -939.4918 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -30.221165 -822.3601 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -22.208208 -604.3163 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -11.181113 -304.2537 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -7.139168 -194.2667 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -5.547182 -150.9466 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -2.819885 -76.7330 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.051361 -28.6090 n=6 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.634671 -17.2703 n=7 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.113734 -3.0949 n=7 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.264220 -7.1898 n=7 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.182418 -4.9638 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.275885 -7.5072 Actinium nbas= 1 z=89. 20 radial functions, spin energy= -0.004 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3443.110473 -93691.8429 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -592.622925 -16126.0971 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -572.762728 -15585.6735 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -147.320745 -4008.8031 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -137.654348 -3745.7670 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -119.541852 -3252.9007 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -36.158308 -983.9180 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -31.761798 -864.2829 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -23.570694 -641.3915 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -12.278273 -334.1089 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -7.713109 -209.8845 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -6.065084 -165.0394 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -3.222784 -87.6964 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.196989 -32.5718 n=6 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.744517 -20.2594 n=6 L=2 occ= 1.00 e= -0.137789 -3.7494 n=7 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.126552 -3.4436 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.533071 -14.5056 n=7 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.455436 -12.3931 n=7 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.344403 -9.3717 Thorium nbas= 2 z=90. 21 radial functions, spin energy= -0.015 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3524.439161 -95904.9100 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -608.351016 -16554.0805 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -588.218147 -16006.2370 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -152.079773 -4138.3029 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -142.255767 -3870.9780 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -123.846510 -3370.0365 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -37.814145 -1028.9757 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -33.325204 -906.8253 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -24.955273 -679.0678 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -13.397442 -364.5631 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -8.287089 -225.5033 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -6.582781 -179.1267 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -3.625762 -98.6620 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.333777 -36.2939 n=6 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.846911 -23.0456 n=6 L=2 occ= 2.00 e= -0.172900 -4.7048 n=7 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.135873 -3.6973 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.588825 -16.0228 n=7 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.484646 -13.1879 n=7 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.366231 -9.9656 n=5 L=3 occ= 0.00 e= -0.834822 -22.7167 Protactinium nbas= 3 z=91. 21 radial functions, spin energy= -0.029 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3606.333728 -98133.3755 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -623.870477 -16976.3867 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -603.470305 -16421.2695 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -156.466762 -4257.6790 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -146.485625 -3986.0784 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -127.781274 -3477.1069 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -39.064548 -1063.0009 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -34.482866 -938.3269 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -25.933200 -705.6786 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -14.105791 -383.8383 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -8.463488 -230.3033 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -6.709782 -182.5825 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -3.659954 -99.5925 n=5 L=3 occ= 2.00 e= -0.316827 -8.6213 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.287240 -35.0276 n=6 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.799746 -21.7622 n=6 L=2 occ= 1.00 e= -0.142484 -3.8772 n=7 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.129654 -3.5281 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.550650 -14.9840 n=7 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.467989 -12.7346 n=7 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.352388 -9.5890 Uranium nbas= 4 z=92. 21 radial functions, spin energy= -0.057 n=1 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -3689.355246 -100392.5070 n=2 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -639.778768 -17409.2735 n=2 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -619.108575 -16846.8087 n=3 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -161.118091 -4384.2482 n=3 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -150.978916 -4108.3471 n=3 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -131.977462 -3591.2910 n=4 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -40.528122 -1102.8268 n=4 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -35.853250 -975.6170 n=4 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -27.123290 -738.0626 n=4 L=3 occ=14.00 e= -15.027502 -408.9193 n=5 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -8.824112 -240.1164 n=5 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -7.018046 -190.9708 n=5 L=2 occ=10.00 e= -3.866198 -105.2046 n=5 L=3 occ= 3.00 e= -0.366558 -9.9746 n=6 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -1.325983 -36.0819 n=6 L=1 occ= 6.00 e= -0.822526 -22.3821 n=6 L=2 occ= 1.00 e= -0.143193 -3.8965 n=7 L=0 occ= 2.00 e= -0.130948 -3.5633 n=6 L=2 occ= 0.00 e= -0.556681 -15.1481 n=7 L=0 occ= 0.00 e= -0.473177 -12.8758 n=7 L=1 occ= 0.00 e= -0.355600 -9.6764

| atoms | basis | points | size (Mb) | float-index (M) | integer-index (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 | 290 | 33491 | 10 | 1 | 200 |
| 98821 | 18 | 2 | 250 | ||
| 58 | 579 | 107840 | 35 | 4 | 300 |
| 209288 | 45 | 5 | 500 | ||
| 88 | 819 | 159348 | 45 | 5 | 500 |
| 319746 | 60 | 7 | 700 | ||
| 123 | 1546 | 254105 | 120 | 14 | 1200 |
| 516647 | 150 | 18 | 1200 |
In Table 8, the first value under "points" refers to the number of points generated using medium mesh, and the second value is the number generated by fine mesh. The size is amount of memory needed by the DMol executable to accommodate this case. The values of float-index and integer-index are those specified near the end of the dmol_memory.dat file, for example:
@float-index: 1250000 @integer-index: 500000 @ratio-index: 20The ratio-index parameter increases the memory dedicated to numerical integration work by the factor ratio-index. If you receive a memory error message such as:
number of integration points exceeds limitThen the ratio-index parameter should be increased, e.g., to 30.
At run time, a C-language malloc statement is used to allocate the memory, based on the values in the dmol_memory.dat file. You may actually obtain more memory than you think are indicated in the dmol_memory.dat file, because C's malloc statement uses a power-of-two scheme. (The file could specify, say, 10 bytes, but you would actually obtain an allocation of 16 (i.e., 24) bytes.)
The .outmol file prints memory-use information for each job. For example:
Memory use data:
...
real array elements available (maxr): 2500000( 19.1 Mb)
minimum real array elements needed: 117440( 0.9 Mb)
real array elements used: 1297080( 9.9 Mb)
Here, the first line shows the value of float-index (and the corresponding size in Mb) used to compile the DMol used in this particular run. The second line shows the absolute minimum memory required to run this job. This must always be less than or equal to float-index. The final line shows the amount of memory actually used in the job. It is usually larger than the minimum required, so that the job runs more efficiently.Recompiling DMol work is no longer needed for working with medium-to-large molecules, since memory is allocated automatically at run time, by reading information from the dmol_memory.dat file. DMol checks the available memory and informs you if there is not enough. A typical message is:
float-index is too small, increase size (pomagn) float-index = 100000 szchk = 120059In this example, this means that before entering the subroutine pomagn, the program required szchk number of words (120059), but only float-index (100,000) were available. To fix this, you need to edit the dmol_memory.dat file and increase float-index to as large as needed. In general, you should make the value of float-index slightly larger (about 20%) than the requested value of szchk. This is because szchk reflects the largest memory requirement so far, that is, up to subroutine pomagn in this example. Subsequent portions of the program might require even more memory.
If you want to change memory allocation, you could make a global or a local change by modifying the dmol_memory.dat file in the release tree's data directory (for a global change) or in your local directory (for a local change). Subsequent DMol runs access the revised dmol_memory.dat file and use the new memory values.
